Psychosis and Dopamine
Pathways
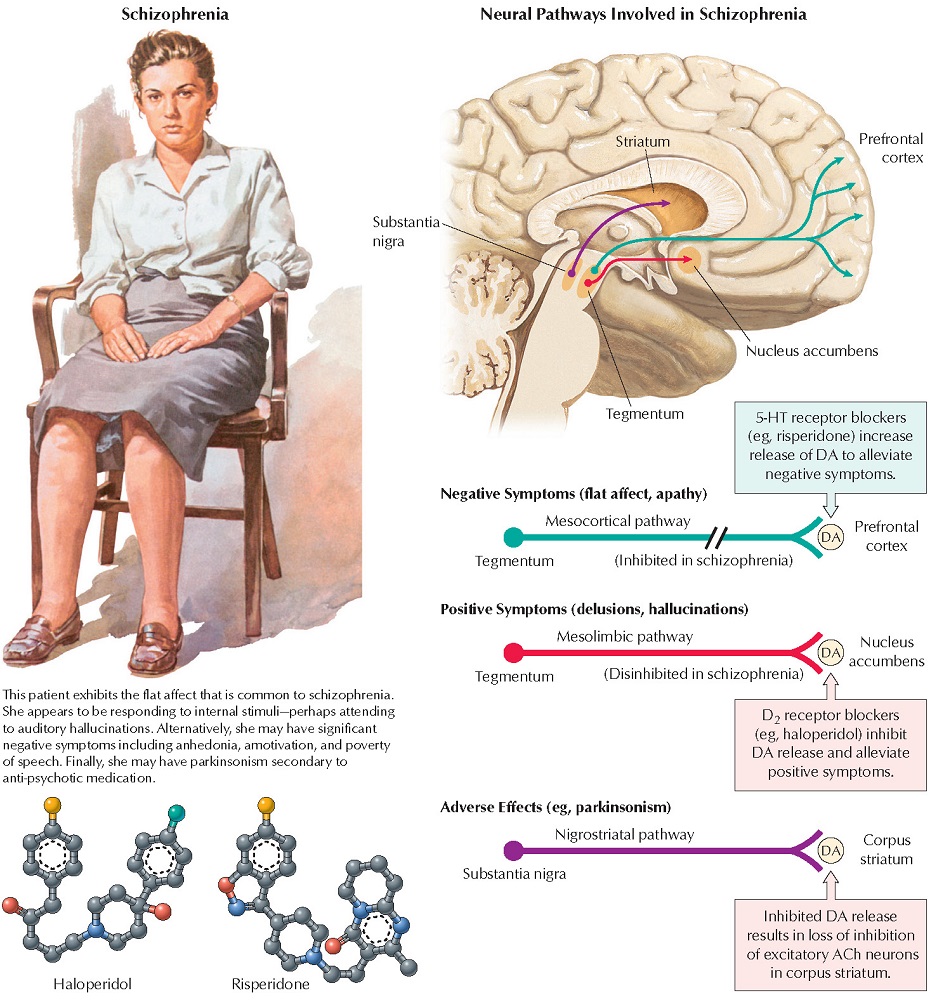
Psychoses are psychogenic mental disorders involving a loss of contact with reality. The most common is schizophrenia, in which perception, thinking, communication, social functioning, and attention are altered. Caused by genetic and environmental factors, it affects approximately 10% of the population. Symptoms are called positive (eg, delusions, hallucinations) or negative (eg, flat affect, apathy); cognitive dysfunction may occur.
Interest in dopamine, 5HT, and Glu
neurotransmitters led to most early drugs’ targeting the
dopamine system, primarily as dopamine D2
receptor antagonists. Typical antipsychotics (eg, chlorpromazine, haloperidol)
are better for treating positive signs than negative signs. For treating
negative signs, the newer (atypical) antipsychotic drugs (eg, clozapine,
risperidone) target other receptors, particularly 5HT. Neurologic (eg,
dystonia, parkinsonism), anticholinergic (eg, blurred vision), and
antiadrenergic (eg, hypotension) adverse effects can
occur.