Sunday, May 18, 2025
Saturday, May 17, 2025
MUSCLES OF THE HAND
Sunday, May 11, 2025
FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR TENDONS OF THE HAND
Monday, April 28, 2025
Friday, April 25, 2025
REPLANTATION
Sunday, April 20, 2025
DIABETIC FOOT ULCERATION
DIABETIC FOOT ULCERATION
 |
| LESIONS OF THE DIABETIC FOOT |
Patients with diabetes are susceptible to a host of foot-related problems. One of the most common and troublesome problems is ulceration and subsequent infection of the foot. Ulceration of the foot develops in the diabetic patient primarily as a result of peripheral neuropathy and loss of the normal protective sensation. Whereas the individual with normal protective sensation would immediately sense minor trauma such as the rubbing of a shoe and take immediate steps to correct it, the diabetic individual is not aware of the problem, allowing the pressure to continue unabated. Eventually, even minor repetitive trauma can result in formation of an ulcer. Ulcers occur most commonly on the weight-bearing plantar surface of the foot and over bony prominences. Once ulceration develops, it is also more likely to become infected in the diabetic patient owing to diminished immune function and impaired circulation. Failure to sense the normal signs of infection due to neuropathy can result in progression to osteomyelitis and extensive, limb-threatening infection in the diabetic patient.
SCOLIOSIS
SCOLIOSIS
Scoliosis is a rotational deformity of the spine and ribs. While in most cases the cause of scoliosis is unknown (idiopathic scoliosis), in excess of 50 genetic markers have been identified as having a major role in adolescent idiopathic curves. Scoliosis may also result from a variety of congenital, neuromuscular, mesenchymal, and traumatic conditions, and it is commonly associated with neurofibromatosis.
Friday, November 22, 2024
KÖHLER DISEASE
KÖHLER DISEASE
 |
Köhler disease is a self-limiting avascular necrosis of the tarsal navicular. It is usually unilateral and most often affects boys around age 4 and also girls around age 5. The navicular is located at the apex of the longitudinal arch of the foot, where it is subjected to repetitive compressive forces during weight bearing. Normally, the navicular is the last bone in the foot to ossify, and irregular ossification is not uncommon, especially in boys. The navicular ossifies later in boys than in girls, and delayed ossification appears to make the navicular more vulnerable to compressive damage.
Wednesday, November 20, 2024
COMMON FOOT INFECTIONS
COMMON
FOOT INFECTIONS
 |
| COMMON INFECTIONS OF FOOT |
The foot exists in an environment that unfortunately can be conducive to infection. Primarily, the use of shoes constricts the foot and produces a warm, moist environment that encourages bacterial growth. Foot infections can occur in all individuals. But, the diabetic patient is particularly susceptible to foot infection owing to the loss of protective sensation. Even trivial trauma either from a poorly fitting shoe or from bare-foot walking can result in violation of the skin and lead to severe infection. Poor blood supply and diminished immune function further compromise the diabetic patient’s ability to fight foot infection. Common locations for foot infections include the paronychial (nail) area and the deep spaces of the foot.
AMPUTATIONS IN THE FOOT
AMPUTATIONS
IN THE FOOT
 |
| AMPUTATION OF FOOT |
Amputation of all or a portion of the foot represents the most elemental form of foot surgery. Often it is disparaged by the surgeon, perhaps because it can be perceived as a failure of treatment. But when performed properly, amputation is truly a reconstructive procedure that can eradicate infection, correct deformity, decrease pain, and improve function.
Thursday, February 16, 2023
Motor Units, Recruitment and Summation
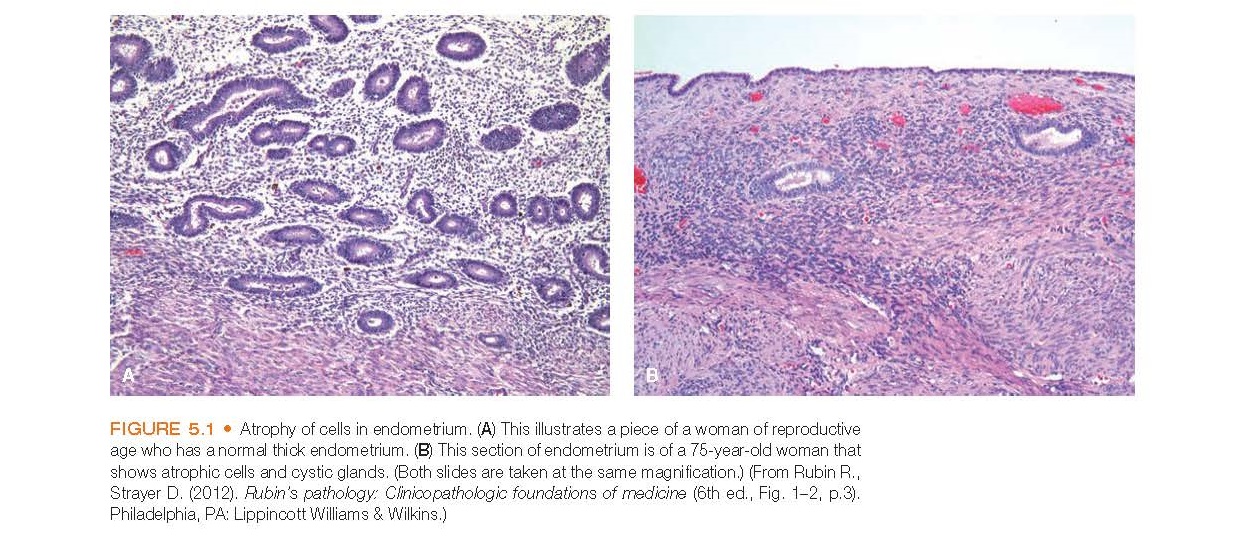
Atrophy
Monday, February 13, 2023
Connective or Supportive Tissue
Wednesday, February 8, 2023
Muscle Tissue
Sunday, February 5, 2023
Skeletal Muscle and its Contraction
Friday, January 20, 2023
SPONDYLOLYSIS AND SPONDYLOLISTHESIS
SPONDYLOLYSIS AND SPONDYLOLISTHESIS
Spondylolysis may represent a stress fracture of the pars interarticularis of the fifth lumbar vertebra. When the fracture allows L5 to slip forward on S1, it is called isthmic spondylolisthesis. Dysplastic, or congenital, spondylolisthesis, in contrast, is due to anomalous development of the posterior structures of the lumbosacral junction.
Thursday, November 10, 2022
DISORDERS OF THE PATELLA
DISORDERS OF THE PATELLA
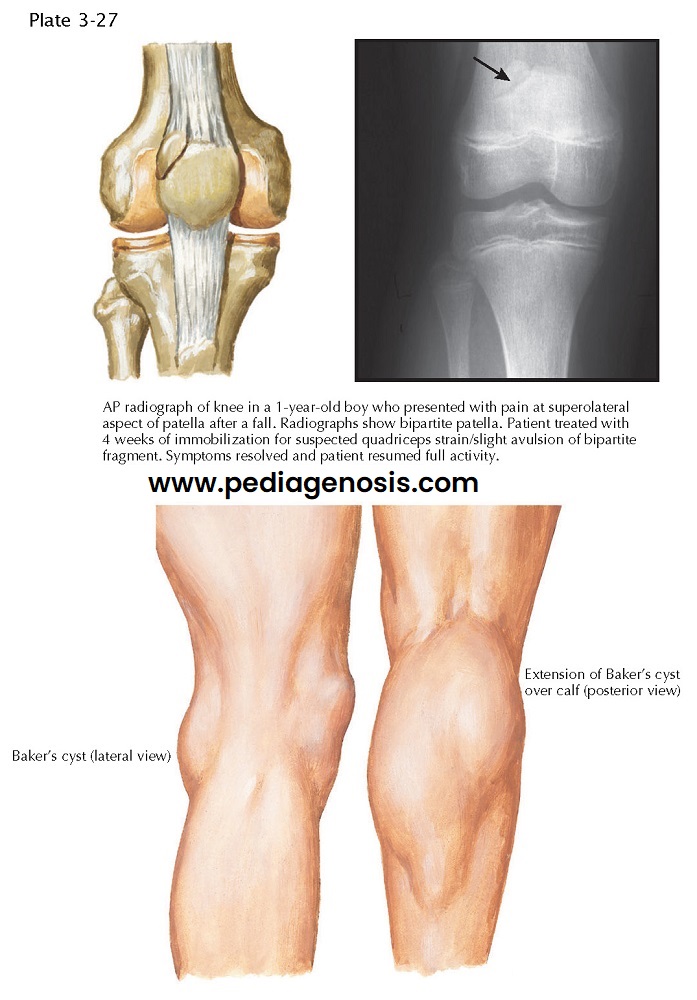 |
| BIPARTITE PATELLA AND BAKER’S CYST |
Congenital fragmentation of the patella is relatively common. One type, bipartite patella, occurs in 1% to 2% of the population. This anatomic variant represents a true synchondrosis (a joint whose surfaces are connected by a cartilaginous plate). Most fragmented patellae remain asymptomatic, but, occasionally, direct trauma to the patella disrupts the synchondroses, causing symptoms that mimic those of a fracture.
Wednesday, September 21, 2022
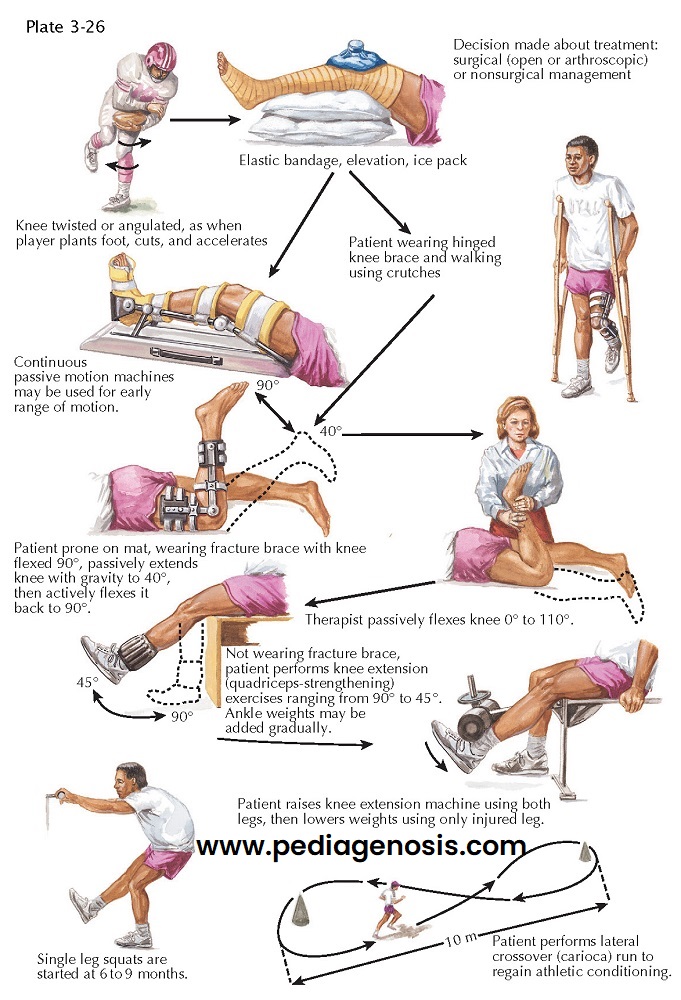
REHABILITATION AFTER SPORTS INJURY
REHABILITATION AFTER SPORTS
INJURY
The goal of conservative management of ligament injuries of the knee is to stabilize the action of the knee with the remaining uninjured, supportive structures. Rehabilitation must begin as soon as possible after injury, because disuse atrophy of the muscles occurs rapidly. Rehabilitation focuses on muscle strengthening, particularly strengthening of the extensor (quadriceps) muscles and the flexor (medial and lateral hamstring) muscles.