UTERINE
INVERSION
Rarely,
the uterus can be turned inside out immediately following the delivery of the
placenta. Uncommon and most often iatrogenic, this may be associated with
catastrophic bleeding and cardiovascular collapse. Incomplete uterine inversion
may also occur. (Rarely the condition has also been reported in nonpregnant
patients with intrauterine pathology such as a pedunculated leiomyomata or
large endometrial polyp.) The prevalence of uterine inversion is estimated to
be about 1 in 6500 to 25,000 deliveries.
Inversion of the uterus can occur because of traction on the umbilical cord or downward pressure on the uterine fundus to facilitate delivery of the placenta. This is more likely to occur with excessive force and a poorly contracted uterus or lower uterine segment. Abnormalities of placentation (placenta accreta, increta, or percreta) can increase the risk of this occurring because of the absence of separation of the placenta from the uterine wall in a normal manner. Risk factors for inversion include uterine atony secondary to multiparity (grand multiparity), uterine overdistension (multiple birth, polyhydramnios), a prolonged labor, prolonged oxytocin stimulation, muscle relaxant agents (such as MgSO4), or rapid labor.
The diagnosis of
inversion of the uterus must be based on a high degree of suspicion. In some
cases, a mass (the uterus) may be seen attached to or directly following the
placenta as it delivers. More often, there is simply brisk bright red vaginal
bleeding accompanied by bradycardia (due to vagal stimulation) and/or tachy-
cardia, hypotension, and vascular collapse due to blood loss. The blood loss
associated with uterine inversion can be catastrophic and is often
underestimated. Uterine inversion must be differentiated from simple uterine
atony following placental delivery, retained placental fragments or undiagnosed
genital tract lacerations, which can generally be accomplished by simple
clinical examination. Although ultrasonography may be used to verify the
diagnosis, this is unnecessary and delays the implementation of therapy.
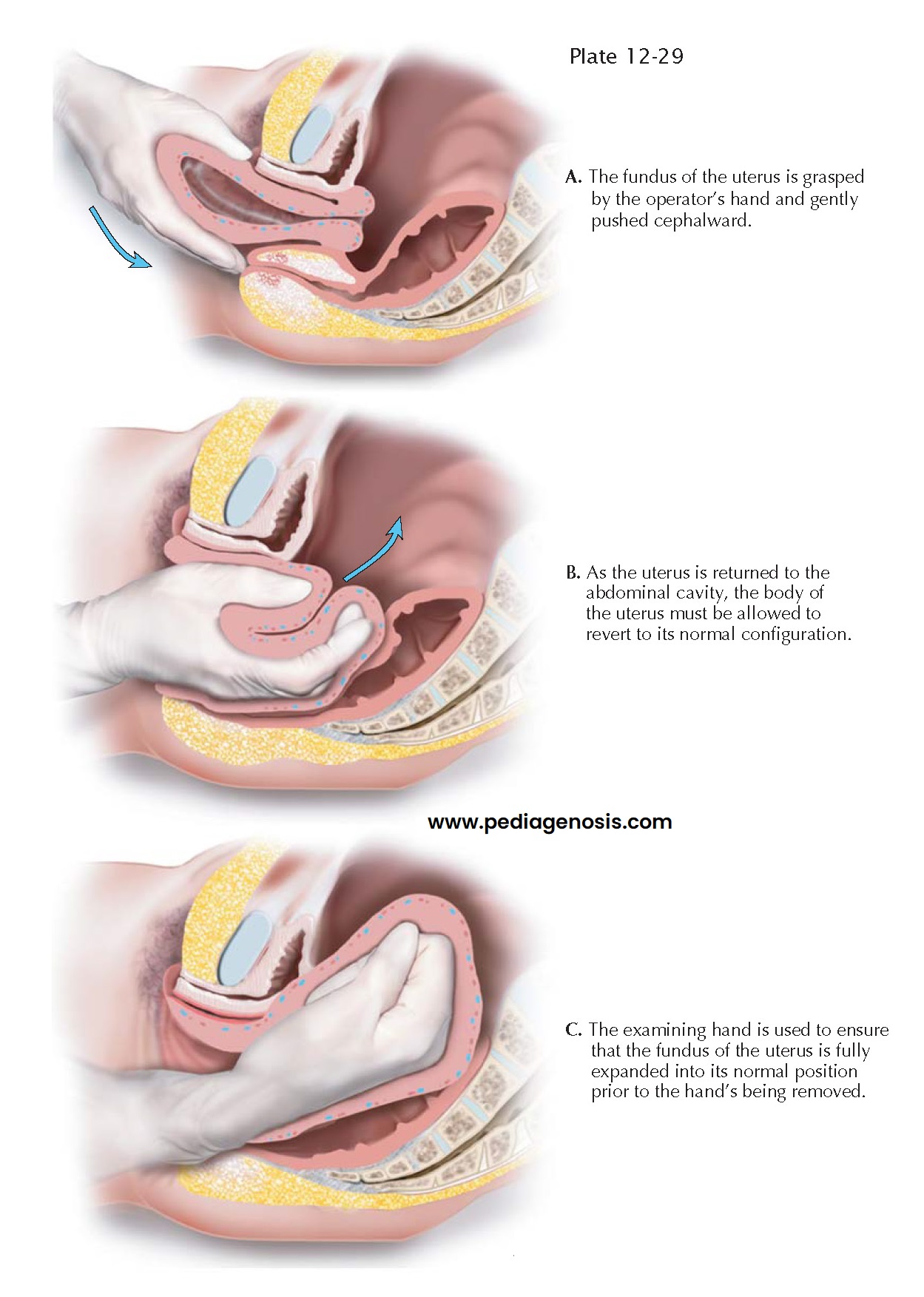
Uterine inversion is
treated by rapid evaluation, fluid support, or resuscitation and calls for
anesthesia assistance. A delay in treatment markedly increases the mortality
rate. Specific treatment is carried out by the use of uterine relaxing agents to
allow the replacement of the uterine fundus (may require general anesthesia
with a relaxant agent such as halothane), and may require operative
intervention (replacement or hysterectomy). Once the uterine wall has relaxed,
gentle manual pressure on the fundus is used to displace it inward and upward
until its normal position can be restored and the uterus returned to its normal
configuration. Uterotonic agents are then used to obtain uterine contraction and
hemostasis. Large-volume fluid replacement should be available and used
liberally if there has been significant blood loss. If the placenta is still
attached to the uterine
wall, it should be left in place until after the uterine fundus has been
reduced and returned to its normal location. Antibiotic prophylaxis should
strongly be considered following the procedure.
If the uterine fundus
cannot be repositioned vaginally through these maneuvers, immediate laparotomy
is necessary. This can allow simultaneous maneuvers from above and below. A
traction suture can sometimes be placed to assist this effort. If a
constriction ring is present
and impeding replacement, the use of local anesthetics to break the muscular
spasm or incision (generally along the posterior aspect of the uterus) may be
needed. The possibility of hysterectomy to control bleeding must always be
considered.
Although unrecognized or untreated uterine inversion can end in hysterectomy, hemorrhagic shock, and cardiovascular collapse, if it is rapidly treated, the outcome is generally good.