DEMENTIA WITH LEWY
BODIES
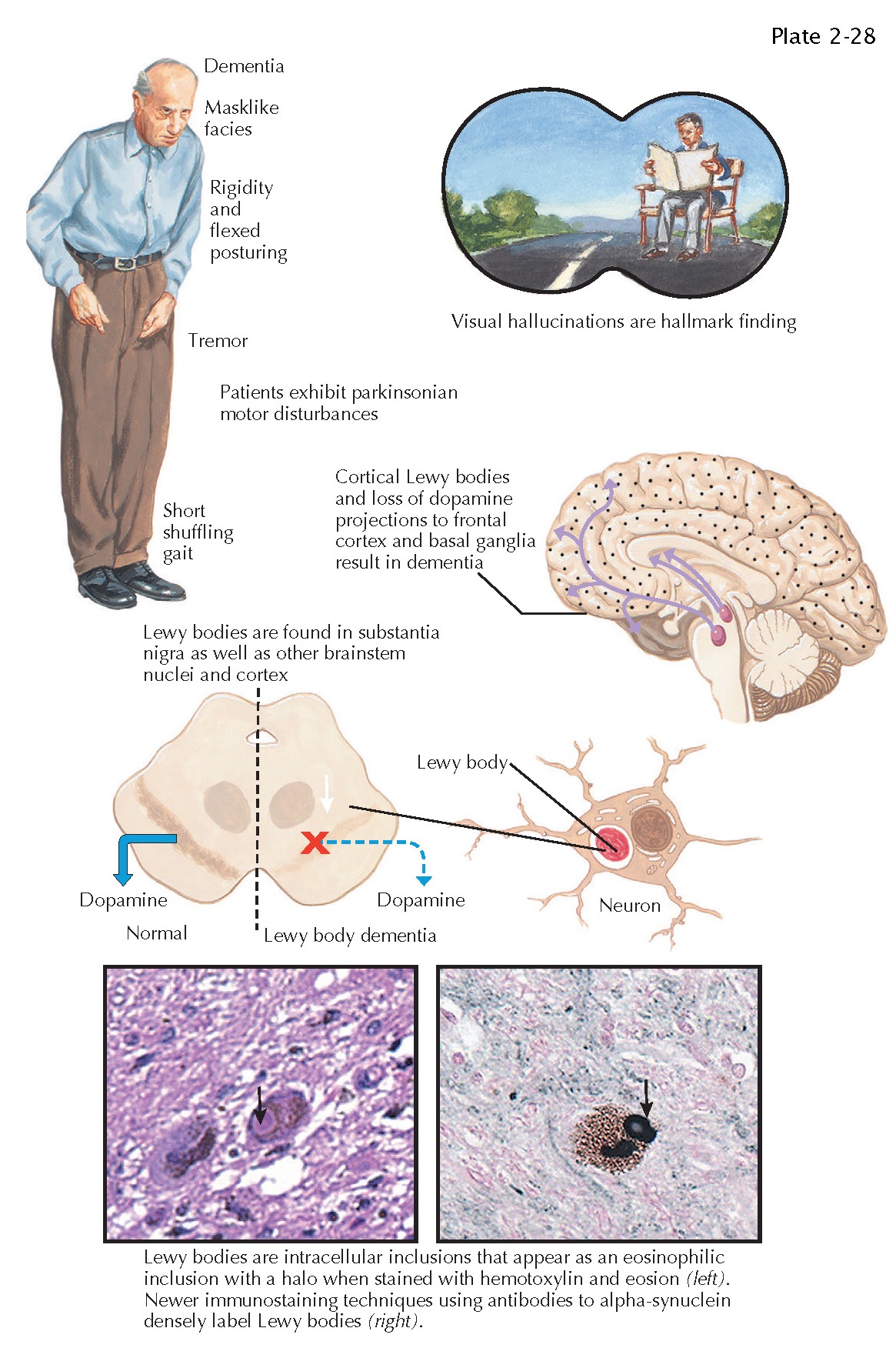
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most common cause of dementia, accounting for 10% to 15% of dementia cases. The pathologic hallmark of DLB is the presence of Lewy bodies in neurons of the brainstem, primarily the substantia nigra, and through-out the cerebral cortex. Lewy bodies are primarily composed of abnormal aggregations of the synaptic protein alpha-synuclein. Interestingly, brain changes of Alzheimer disease (plaques and tangles) frequently co-occur with typical Lewy body pathology.
In patients with DLB, the cognitive
and functional decline of dementia is accompanied by a combination of clinical
features that include visual hallucinations, parkinsonism, and fluctuating
cognitive impairment. Visual hallucinations may present early in the clinical
course and tend to persist throughout the course. Typically, the visual
hallucinations are vivid images of animate objects (e.g., children, animals) as
opposed to nonspecific visual phenomena. Parkinsonism (rigidity, tremor,
bradykinesia, gait abnormalities) develops in most DLB patients at some time in
the course of the disease. Individuals with DLB
typically present with recurrent episodes of confusion on a background of
progressive deterioration. The fluctuations in cognitive function are manifest
as shifting attention and levels of alertness that may vary over minutes,
hours, or days.
Other features that are commonly
observed in DLB patients include additional neuropsychiatric symptoms of
delusions, apathy, and anxiety. Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior
disorders are frequently seen in
DLB and other synucleinopathies such
as Parkinson disease. REM sleep behavior disorders are manifested as vivid or
frightening dreams associated with simple or complex motor behavior.
Additionally, autonomic abnormalities are common in DLB and include orthostatic
hypotension and carotid-sinus hypersensitivity. These abnormalities can result
in “dizziness,” presyncope, syncope, and falls as common aspects of the
clinical presentation.